CO2 FOOTPRINT REDUCTION
High value creation, low emissions


Our Goal
Climate neutrality of All sites by 2035
Sustainability is a cornerstone of our corporate strategy, with a clear goal to achieve climate neutrality by 2035
To reach this, we are thoroughly analyzing our entire value chain and implementing targeted actions to minimize both direct and indirect emissions. Initially, we are focusing on optimizing operations at our own sites, addressing production processes (Scope 1) and energy consumption.
We are relentlessly refining our processes to conserve raw materials, enhance energy efficiency, minimize waste, and accelerate the transition to a circular economy.
We are continuously optimizing our processes to actively save raw materials and energy, reduce waste, and increasingly enable recycling and circular economy.
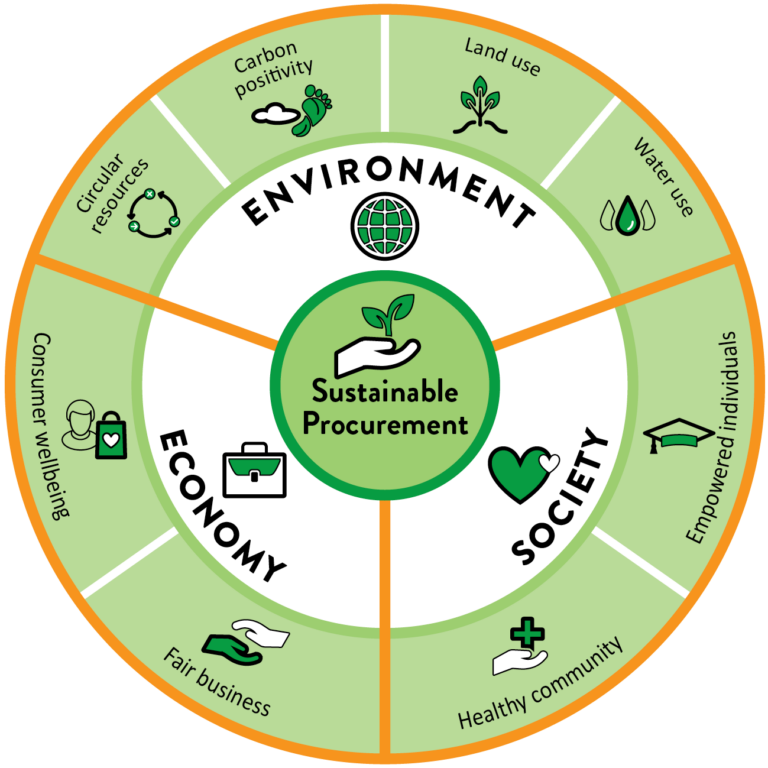
-Sustainable Procurement-
Sustainable procurement refers to the process of sourcing goods and services in a way that promotes environmental, social, and economic sustainability. This aligns with the UN’s definition of sustainability and John Elkington’s “Triple Bottom Line,” which introduces three core elements:
People (Social Responsibility): Ensuring that suppliers uphold fair labor practices, human rights, and community well-being, while promoting diversity and inclusion in the supply chain.
Planet (Environmental Stewardship): Selecting products and services that minimize environmental impact, such as reducing resource consumption, waste, and carbon emissions, while promoting recycling and circular economy principles.
Profit (Economic Viability): Securing cost-effective procurement while ensuring long-term value through ethical sourcing, risk management, and supporting suppliers committed to sustainable practices.
Sustainable procurement ensures that businesses not only meet their immediate needs but also contribute to the broader goals of environmental preservation, social equity, and economic stability.
The three core elements of sustainable procurement are reflected in the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). For example, the social aspect aligns with SDG 1: No Poverty, focusing on fair labor practices and supporting communities. The economic aspect relates to SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth, ensuring safe working conditions and driving economic development. The environmental aspect corresponds to SDG 14: Life Below Water, which emphasizes reducing pollution and safeguarding marine ecosystems
The largest portion of our carbon footprint originates from Scope 3, which encompasses various indirect emissions. For us, this primarily relates to the procurement of raw materials, as well as logistics, business travel, and waste. We understand that sourcing raw materials can have a significant impact on the environment, and therefore, we are committed to ensuring that our supply chain operates sustainably.
To mitigate this impact, we prioritize working with suppliers who share our commitment to sustainable sourcing. We ensure that the materials we purchase are responsibly obtained, and that their mining and processing are carried out in a way that minimizes harm to the environment. This includes choosing suppliers who adopt best practices in reducing resource consumption, protecting ecosystems, and adhering to ethical labor standards.
By focusing on these practices, we aim to reduce the environmental footprint of our entire value chain, contribute to the circular economy, and promote long-term sustainability. This approach not only helps us address our carbon footprint but also fosters a more sustainable and responsible supply chain, aligned with our broader environmental goals.
